#agricultural biodiversity
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The argan tree as a fundamental pillar for sustainable development.

The argan tree is typically a multipurpose tree that supports income generation, increases resilience and improves climate adaptation, playing a very important role in achieving the three dimensions of sustainable development - economic, social and environmental - at the local level.
The sustainable argan production sector contributes to the economic empowerment and financial inclusion of local communities, especially women living in rural areas. Cooperatives are instrumental in promoting local job opportunities and can play an important role in contributing to food security and in eradicating poverty.
For centuries, the argan tree has been a mainstay of the Berber and Arab-origin indigenous rural communities, which developed a specific culture and identity, sharing their traditional knowledge and skills through non-formal education, particularly the unique knowledge associated with the traditional production of argan oil by women.
The unique argan-based agro-forestry-pastoral system uses only locally adapted species and pastoralism activities and relies on traditional water management provided by the Matifiya - a rain water reservoir carved into rock, hence contributing to climate change mitigation and adaptation, and to the conservation of biodiversity. United Nations on International Day of Argania
#argan-based agro-forestry-pastoral systel#argania tree#argania#argan forest#argan ecosystem#argan tree#traditional water management#rain water reservoir#agricultural biodiversity#climate change mitigation#argan species#sustainable development#International Day of Argania#10 may
0 notes
Text


🌱✨️ "Living Soil" Embroidered Crewnecks & Hoodies ✨️🌱
Stay cozy while supporting soil health and sustainable farming 💚💛❤️
🌟 when you sign up for email offers and updates on our website, you get a chance to win up to 50% OFF your order!
🌟 FREE SHIPPING for orders over $50!!!
#soil health#soil science#soil#permaculture#environmental education#enviroment art#regenerative agriculture#regenerative farming#agriculture#sustainable living#sustainable farming#sustainability#organic life#organic matter#organic lifestyle#organic farming#organic#compost lifestyle#composting#compost#vermicompost#biodiversity#ecomindset#conservation#microbes#plant life#plant lover#street style#hippie#stoner society
537 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Despite the Central Appalachia ecosystem being historically famous as coal country, under this diverse broadleaf canopy lies a rich, biodiverse world of native plants helping to fill North America’s medicinal herb cabinet.
And it turns out that the very communities once reliant on the coalfields are now bringing this botanical diversity to the country.
“Many different Appalachian people, stretching from pre-colonization to today, have tended, harvested, sold, and used a vast number of forest botanicals like American ginseng, ramps, black cohosh, and goldenseal,” said Shannon Bell, Virginia Tech professor in the Dept. of Sociology. “These plants have long been integral to many Appalachians’ livelihoods and traditions.”
50% of the medicinal herbs, roots, and barks in the North American herbal supply chain are native to the Appalachian Mountains, and the bulk of these species are harvested or grown in Central Appalachia, which includes southern West Virginia, eastern Kentucky, far-southwest Virginia, and east Tennessee.
The United Plant Savers, a nonprofit with a focus on native medicinal plants and their habitats, has identified many of the most popular forest medicinals as species of concern due to their declining populations.
Along with the herbal supply chain being largely native to Appalachia, the herb gatherers themselves are also native [to Appalachia, not Native American specifically], but because processing into medicine and seasonings takes place outside the region, the majority of the profits from the industry do too.
In a press release on Bell’s superb research and advocacy work within Appalachia’s botanical communities, she refers back to the moment that her interest in the industry and the region sprouted; when like many of us, she was out in a nearby woods waiting out the pandemic.
“My family and I spent a lot of time in the woods behind our house during quarantine,” Bell said. “We observed the emergence of all the spring ephemerals in the forest understory – hepatica, spring beauty, bloodroot, trillium, mayapple. I came to appreciate the importance of the region’s botanical biodiversity more than ever, and realized I wanted to incorporate this new part of my life into my research.”
With co-investigator, John Munsell at VA Tech’s College of Natural Resources and Environment, Bell’s project sought to identify ways that Central Appalachian communities could retain more of the profits from the herbal industry while simultaneously ensuring that populations of at-risk forest botanicals not only survive, but thrive and expand in the region.
Bell conducted participant observation and interviews with wild harvesters and is currently working on a mail survey with local herb buyers. She also piloted a ginseng seed distribution program, and helped a wild harvester write a grant proposal to start a forest farm.
“Economic development in post-coal communities often focuses on other types of energy development, like fracking and natural gas pipelines, or on building prisons and landfills. Central Appalachia is one of the most biodiverse places on the planet. I think that placing a greater value on this biodiversity is key to promoting a more sustainable future for the region,” Bell told VA Tech press.
Armed with a planning grant of nearly half a million dollars, Bell and collaborators are specifically targeting forest farming as a way to achieve that sustainable future.
Finally, enlisting support from the nonprofit organization Appalachian Sustainable Development, Virginia Tech, the City of Norton, a sculpture artist team, and various forest botanicals practitioners in her rolodex, Bell organized the creation of a ‘living monument’ along Flag Rock Recreation Area in Norton, Virginia.
An interpretive trail, the monument tells the story of the historic uses that these wild botanicals had for the various societies that have inhabited Appalachia, and the contemporary value they still hold for people today."
-via Good News Network, September 12, 2024
#appalachia#united states#biodiversity#herbs#herbal medicine#herbalism#native plants#conservation#sustainability#sustainable agriculture#solarpunk#good news#hope
712 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay. So you know how industrial agriculture overuses synthetic fertilizers loaded with nitrogen to make up for the decades of soil degradation that intensive farming practices cause? So not only does a lot of this fertilizer end up as runoff in our waterways every time it rains, but while it's still on land it's messing with the surrounding ecology, particularly plants.
See, nitrogen normally exists primarily in our atmosphere, and most organisms can't absorb atmospheric nitrogen, even though it's a crucial nutrient. However, some soil bacteria are capable of drawing this nitrogen in and converting it to a form of ammonia accessible to plants. These bacteria can be found in little nodules of many plants' roots, and make the nitrogen available to their hosts in return for a nice safe place to live. When these nitrogen-fixing plants shed leaves or other parts, or die entirely, the nitrogen in their tissues is then released into the local ecosystem as they decay.
However, when we started supercharging farmland and gardens with tons of extra nitrogen through fertilizers, we threw off the entire nitrogen cycle. Plants native to a given ecosystem have evolved to tolerate a certain balance of nutrients, to include some that may be naturally scarce, and when the nutrient balance suddenly shifts significantly, it causes a lot of upset. With more nitrogen filtering through nearby ecosystems, and those downstream, nitrogen-fixing plants are suddenly losing their competitive edge, and are becoming less common in these places. Over time, they can become locally extinct, breaking whatever bonds they had with other species in the ecosystem, which often leads to even more ecological unraveling.
So you see, more fertilizer isn't always the answer. When engaging in habitat restoration efforts in many parts of the United States, it's important to work with the native soil instead of adding a lot of amendments. Those amendments can actually make it easier for invasive weeds to get a roothold because they often come from places with richer soil, or are simply more able to make the most of the excess nutrients to grow faster and out-compete native plants. Adding too much nitrogen, whether intentionally or as a byproduct of agriculture, makes it even tougher for native ecosystems to thrive in disturbed areas adjacent to farms. On the other hand, making sure your restoration site has native nitrogen-fixers and other pioneer plants helps set the stage for long-term success, while making conditions less favorable to nutrient-hungry invasive species.
We already had plenty of reason to curb the overuse of synthetic fertilizers; this study just adds another argument in that regard.
#plants#botany#plantblr#farming#agriculture#sustainability#permaculture#nature#ecology#restoration ecology#habitat restoration#pollution#environment#conservation#native plants#native species#invasive species#ecosystems#science#scicomm#biodiversity
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
Back from the dead: the ‘zombie’ ponds repumping nature into Essex farmland
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
We have had 3 hard frosts and the veggies still pull through. It pays to save your seeds as seeds have a memory.
Booking tours now through mid April 2025.

#visionarygrowingsolutions#compost#atlanta urban ag#simplefoodsmallfarmz#winter growing#atlanta airbnd experience#air bnb experience atlanta#biodynamic#soil#biodiversity#permaculture#urban ag#food systems#soil health#simple food small farmz air bnb agriculture experience#atlanta air bnb urban agriculture experence#airbnb experience#seed saving#winter crops#swiss chard#maurice small
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
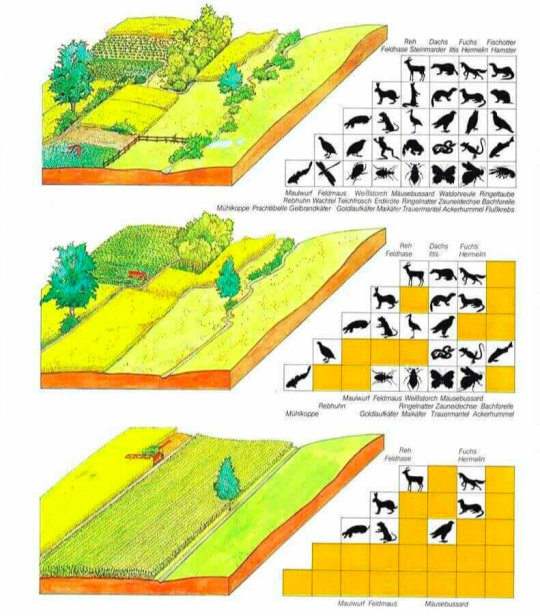
Diverse, well-integrated farms like coltura promiscua support significantly more native biodiversity than modern monocultures. Source: BUNDESAMT, F. U., & LANDSCHAFT, W. U. (1997). Umwelt in der Schweiz 1997. Berna, Buwal.
94 notes
·
View notes
Text

The surprising diversity of Pineapples (Ananas comosus).
The Active Pineapple Germplasm Bank (Pineapple AGB) of Embrapa Cassava & Fruits (Embrapa/ CNPMF) has more than 700 accessions under field conditions. As backups, there are copies kept in a greenhouse, with one or two plants per accession, cultivated in plastic pots with commercial substrate. An in vitro gene bank was established in 2003, and during the past few years, several studies have been carried out to improve the in vitro conservation protocol. Currently, about 60% of the AGB’s accessions are preserved by this protocol. Another conservation strategy used is cryopreservation of shoot tips and pollen grains, with well-defined methods. One of the most significant advances in the pineapple germplasm conservation has been the implementation of a quality control system, which enabled to define standard operation procedures (SOP) towards a more efficient and safer germplasm conservation.
Source:
Vidigal Souza, Fernanda & Souza, Everton & Aud, Fabiana & Costa, Eva & Silva, Paulo & Andrade, Eduardo & Rebouças, Danilo & Andrade, Danilo & Sousa, Andressa & Pugas, Carlos & Rebouças, Érica & França, Beatriz & França, Rivã. (2022). Advances in the conservation of pineapple genetic resources at Embrapa Cassava and Fruits. 28. 28-33.
#katia plant scientist#botany#plant biology#plant science#plants#fruit#pineapple#pineapples#biodiversity#agriculture#conservation#genetic diversity#sustainable agriculture#tropical plants#science#biology
328 notes
·
View notes
Text
Experts Demonstrate How Solar Farms Can Become Hubs for ‘Biodiversity Enhancement’ at Every Level https://www.goodnewsnetwork.org/experts-uncover-side-effects-of-solar-farms-they-become-hubs-for-biodiversity-enhancement/
#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#solar farms#solar panels#solar energy#green energy#green technology#agriculture#biodiversity
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

Took this photo on 1-5-2025 in the a.m.. These herbs and veggies have survived 2 hard frosts thus far in early winter. The next 10 nights will be at or below 26 degrees for multiple hours. I’m curious how these seed saved plants will do. They have a great memory of previous years of cold so fingers crossed for stronger plants in late February.
#atlanta airbnd experience#airbnb experience#frost#atlanta airb experience#tending to the herbs#atlanta airbnb agricultural experience#visionary growing solutions#atlanta urban ag#biodiversity#biodynamic#herbs#permaculture#simple food small farmz#simplefoodsmallfarmz#simple food#winter#zone 8a#maurice small
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
May 10th as International Day of Argania.

This unique region, where argan trees have been cultivated for centuries combines agricultural biodiversity, resilient ecosystems and valuable cultural heritage. For that reason, it has gotten recognition and protection from various UN entities.
The United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) designated in 1988 the endemic production area as the Arganeraie Biosphere Reserve. Also, all know-how concerning the argan tree was inscribed in 2014 on the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
Moreover, in December 2018, FAO recognized the Argan-based agro-sylvo-pastoral system within the area of Ait Souab - Ait Mansour in Morocco as a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System.
And lastly, in 2021, the United Nations General Assembly proclaimed 10 May the International Day of Argania. The resolution, submitted by Morocco, was co-sponsored by 113 member states of the United Nations and adopted by consensus.
#Arganeraie Biosphere Reserve#10 may#ARGANIA#International day of Argania#united nations general assemly#agro-sylvo-pastoral system#Argan-based#agricultural biodiversity#resilient ecosystems#sustainable cultivation practices#cultivating#United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)#argan forest#argan ecosystem#argania tree#argan species#argan tree
0 notes
Text

Isopods, aka roly-polies or pill bugs, - tiny crustaceans with BIG impacts
They’re detritivores, meaning they feast on dead and decaying organic matter—like fallen leaves, wood, and even fungi. 🍂🥀🪵
Here’s why they’re vital for our soil:
🌱 Nutrient Recycling: As they munch through plant material, they break it down into smaller particles, speeding up the decomposition process. This enriches the soil with vital nutrients that plants need to thrive.
🔄 Carbon Cycling: By decomposing organic material, isopods play a key role in the carbon cycle, helping store carbon in the soil and reducing carbon loss to the atmosphere.
🌍 Soil Aeration: While burrowing and feeding, isopods loosen compacted soil, improving oxygen flow and creating a healthier environment for plant roots and microorganisms.
Found on every continent except Antarctica, isopods thrive in forests, gardens, and even urban environments. 🌟 Wherever there’s organic matter to break down, these hardworking decomposers are on the job!
So next time you see an isopod, give it some love! 🤍 They’re working hard to keep our soil alive and thriving. 🌿
#soil health#soil science#soil#permaculture#isopods#pill bug#roly poly#environmental education#environmental awareness#regenerative farming#regenerative agriculture#agriculture#sustainable living#sustainable farming#sustainability#organic life#organic matter#organic lifestyle#organic farming#organic#vermicompost#composting#compost lifestyle#compost#biodiversity#conservation#ecomindset#bugs#insects#nature lovers
75 notes
·
View notes
Note
weird question, but do you know if regenerative agriculture is growing, and by what rate? it's important to me but looking for articles on my own can trigger a panic attack :[ no worries if not !

Hey! Thank you so much for asking. Honestly, agriculture and sustainable agriculture specifically are very close to my heart as well, so I was glad for the excuse to do some research :)
Also, thank you for your patience, I know you sent this Ask a bit ago. It’s good that you’re listening to yourself and not going around searching for things that might cause you harm, so thanks again for reaching out!
So, what is regenerative agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture is a way of farming that focuses on soil health. When soil is healthy, it produces more food and nutrition, stores more carbon and increases biodiversity – the variety of species. Healthy soil supports other water, land and air environments and ecosystems through natural processes including water drainage and pollination – the fertilization of plants.
Regenerative agriculture is a defining term for sustainability in our food system - while there is no one true definition of regenerative agriculture, the concept has been around for centuries, taking root in Indigenous growing practices. Regenerative approaches can bolster soil health and watershed health. They can also add to climate mitigation and potentially tie into regulatory or commercial incentives for a more sustainable diet.
Regenerative farming methods include minimizing the ploughing of land. This keeps CO2 in the soil, improves its water absorbency and leaves vital fungal communities in the earth undisturbed.
Rotating crops to vary the types of crop planted improves biodiversity, while using animal manure and compost helps to return nutrients to the soil.
Continuously grazing animals on the same piece of land can also degrade soil, explains the Regenerative agriculture in Europe report from the European Academies’ Science Advisory Council. So regenerative agriculture methods include moving grazing animals to different pastures.
How can it help?
Regenerative farming can improve crop yields – the volume of crops produced – by improving the health of soil and its ability to retain water, as well as reducing soil erosion. If regenerative farming was implemented in Africa, crop yields could rise 13% by 2040 and up to 40% in the future, according to a Regenerative Farming in Africa report by conservation organization the International Union for Conservation of Nature and the UN.
Regenerative farming can also reduce emissions from agriculture and turn the croplands and pastures, which cover up to 40% of Earth’s ice-free land area, into carbon sinks. These are environments that naturally absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, according to climate solutions organization Project Drawdown.
5 ways to scale regenerative agriculture:
1. Agree on common metrics for environmental outcomes. Today, there are many disparate efforts to define and measure environmental outcomes. We must move to a set of metrics adopted by the whole food industry, making it easier for farmers to adjust their practices and for positive changes to be rewarded. 2. Build farmers’ income from environmental outcomes such as carbon reduction and removal. We need a well-functioning market with a credible system of payments for environmental outcomes, trusted by buyers and sellers, that creates a new, durable, income stream for farmers. 3. Create mechanisms to share the cost of transition with farmers. Today, all the risk and cost sits with the farmers. 4. Ensure government policy enables and rewards farmers for transition. Too many government policies are in fact supporting the status quo of farming. The food sector must come together and work jointly with regulators to address this. 5. Develop new sourcing models to spread the cost of transition. We must move from sourcing models that take crops from anywhere to models that involve collaboration between off-takers from different sectors to take crops from areas converting to regenerative farming.
The rise of regenerative agriculture
In 2019, General Mills, the manufacturer of Cheerios, Yoplait and Annie’s Mac and Cheese (among other products), announced it would begin sourcing a portion of its corn, wheat, dairy and sugar from farmers who were engaged in regenerative agriculture practices and committed to advancing the practice of regenerative agriculture on one million acres of land by 2030. In early 2020, Whole Foods announced regenerative agriculture would be the No. 1 food trend and, in spite of the pandemic and the rapid growth of online shopping overshadowing the trend, business interest in the field still spiked by 138%.
More recently, PepsiCo announced it was adopting regenerative agriculture practices among 7 million acres of its farmland. Cargill declared it intends to do the same on 10 million acres by 2030, and Walmart has committed to advancing the practice on 50 million acres. Other companies pursuing regenerative agriculture include Danone, Unilever, Hormel, Target and Land O’ Lakes.
According to Nielsen, 75% of millennials are altering their buying habits with the environment in mind. This sentiment, of course, does not always materialize into tangible actions on behalf of every consumer. However, it is clear from the actions of PepsiCo, General Mills, Walmart, Unilever and others that they believe consumers’ expectations of what is environmentally friendly are shifting and that they will soon be looking to purchase regeneratively-produced foods because of the many benefits they produce.
The next step in the transition to regenerative agriculture is certification. The goal is to create labeling that will allow the consumer to connect to the full suite of their values. Some companies are partnering with nonprofit conveners and certifiers. The Savory Institute is one such partner, convening producers and brands around regenerative agriculture and more holistic land management practices.
In 2020, the Savory Institute granted its first “Ecological OutCome Verification (EOV) seal to Epic’s latest high protein bars by certifying that its featured beef was raised with regenerative agriculture practices.
The program was developed to let the land speak for itself by showing improvement through both leading and lagging functions such as plant diversity and water holding capacity. There are now thousands of products that have been Land to Market verified, with over 80 brand partnerships with companies such as Epic Provisions, Eileen Fisher and Applegate. Daily Harvest is giving growers in that space three-year contracts as well as markets and price premiums for the transitional crop. It's focusing on that transitional organic process as a stepping stone toward a regenerative organic food system.
Daily Harvest’s Almond Project creates an alliance with the Savory Institute and a group of stakeholders - including Simple Mills and Cappello’s - to bring regenerative practices to almonds in the Central Valley of California.
These companies are working with Treehouse California Almonds, their shared almond supplier, to lead soil health research on 160 acres of farmland. Over five years, the Project will focus on measuring outcomes around the ecosystem and soil health of regenerative practices – comparing those side by side with neighboring conventional baselines.
“We need industry partnership; we need pre-competitive collaboration,” says Rebecca Gildiner, Director of Sustainability at Daily Harvest, of the Almond Project. “Sustainability cannot be competitive. We are all sharing suppliers, we are all sharing supply – rising tides truly lift all boats. The industry has to understand our responsibility in investing, where historically investments have disproportionately focused on yields with a sole focus of feeding the world. We know this has been critical in the past but it has overlooked other forms of capital, other than financial. We need to look towards experimenting in holistic systems that have other outcomes than yield and profit - instead of saying organic can’t feed the world, we have to invest in figuring out how organic can feed the world because it’s critical.”
////
In short!!!
Many articles are stating regenerative agriculture as a defining, and rising “buzz word” in the industry. It seems that consumers are becoming more and more aware and are demanding more sustainable approaches to agriculture.
We, of course, have a way to go, but it seems from the data that I’ve gathered, that regenerative agriculture is, in fact, on the rise. Demand is rising, and many are working on ways to globalize those methods.
Source Source Source Source
#climate change#climate#hope#good news#climate news#climate crisis#more to come#climate emergency#news#climate justice#agriculture#ecosystem#farming#conservation#biodiversity#regenerative agriculture
93 notes
·
View notes
Text

Follow the positive dreams because dreams turn into reality.
#house plants#plant propagation#tending to the herbs#oregano#pathos#tradescantia#compost#visionary growing solutions#permaculture#biodynamic#soil#atlanta urban ag#recycle#food systems#urban ag#soil food web#biodiversity#airbnb experience Atlanta#simple food small farmz#regenerative agriculture#maurice small
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Biodiversity loss in agriculture is a pressing threat to global food systems, reducing our ability to cope with climate change, environmental degradation, and nutritional challenges. Over the past century, about 75% of plant genetic diversity has been lost as farmers have shifted toward high-yielding, genetically uniform crops. Today, just nine plant species account for 66% of global crop production, with rice, wheat, and maize alone providing more than 50% of the world’s plant-derived calories. This reliance on a narrow set of crops undermines food system resilience, leaving us vulnerable to pests, diseases, and climate extremes. It has also created a monocultural vulnerability reminiscent of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, when reliance on a single, genetically uniform crop led to catastrophic losses due to disease. Genetic diversity within and among species acts as a natural buffer against environmental changes. Different crop varieties respond differently to stressors, providing farmers with options to manage risks. When one crop fails, others can compensate, helping to safeguard harvests and livelihoods. However, as the diversity on our farms diminishes, farmers have fewer tools to adapt to the growing volatility brought on by climate change. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and heat waves are becoming more severe, and monocultures are ill-equipped to withstand these shocks. The environmental impact of current agricultural practices further exacerbates biodiversity loss. Agriculture is responsible for about 90% of global deforestation and contributes substantially to habitat destruction, driving the extinction of countless species. Excessive use of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides pollutes soils and waterways, disrupting ecosystems and degrading essential natural services such as pollination and soil fertility. Soil degradation now affects one-third of the world’s soils. In sub-Saharan Africa, agriculture is responsible for 80% of soil degradation on farmland, leading to reduced plant diversity because only the few species that can tolerate poor soil conditions survive. Moreover, the heavy use of nitrogen fertilizers and livestock manure, particularly in regions such as Asia and Latin America, has disrupted natural nitrogen cycles, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions such as nitrous oxide and methane. These emissions not only drive climate change but also accelerate biodiversity loss by reducing the resilience and health of ecosystems. The decline of agricultural biodiversity also impacts human health. Diets worldwide have become increasingly homogeneous, dominated by a few staple crops that are energy-rich but nutrient-poor. Less than 200 species currently contribute to global food supplies, and this lack of variety has serious health consequences. Low dietary diversity is now a leading driver of diet-related deaths, with about 11 million premature deaths annually linked to unhealthy diets. The decline in biodiversity means that fewer nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds are available, exacerbating malnutrition in all its forms, from undernutrition to obesity.
10 October 2024
63 notes
·
View notes
